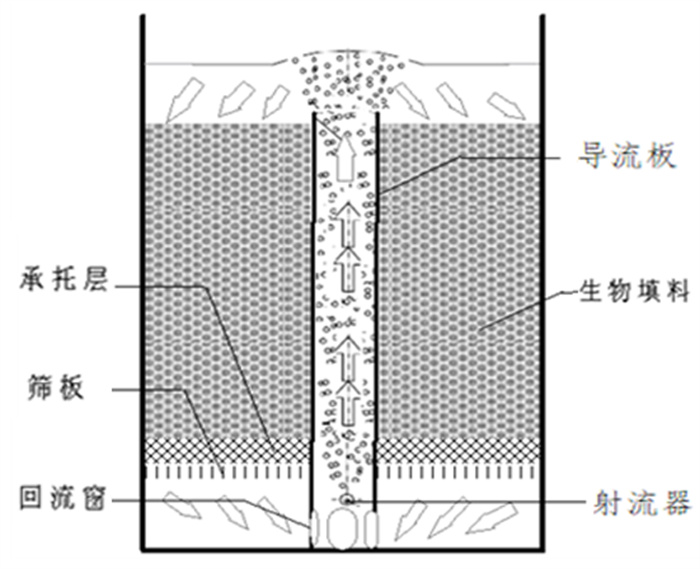
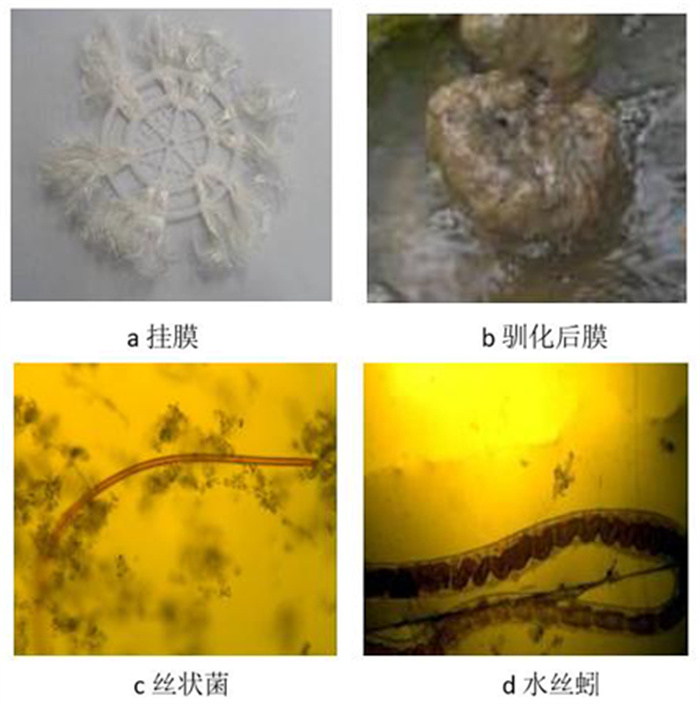
Ozone Oxidation-biochemical Method Combined Treatment of Fankou Lead-zinc Mine Wastewater and Recycling
-
摘要:
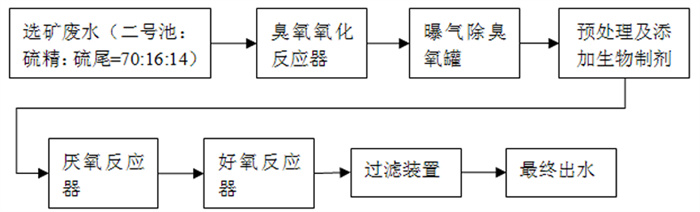
基于凡口铅锌矿选矿废水特性的解析及技改需要,以"初期氧化+预处理+生化处理法"工艺处理选矿废水。通过研究不同O3浓度、催化氧化时间和不同水力停留时间(HRT)对废水处理效果的影响,考察处理后废水回用对选矿指标的影响,评估该工艺的可行性。结果表明,初期氧化阶段,利用O3直接或间接氧化废水中残留药剂;协同预处理去除废水中Ca2+和重金属;后续的生化处理进一步提升出水质量。在O3浓度为60 mg/L,催化氧化时间为20 min,水力停留时间为16.71 h,能够将废水COD浓度降至为34.32 mg/L,去除率为91.9%;HRT和O3浓度的增加对废水处理效果显著;将处理后废水回用于选矿工艺,与清水的选矿指标接近。该工艺在运行稳定下不仅能够实现选矿废水高效处理和回用,处理成本较低为2.65元/m3,该工艺可为国内类似铅锌选厂废水的处理及回用提供借鉴。
Abstract:This study was analyzing the beneficiation wastewater of Fankou lead-zinc mine and meeting the technical upgrade requirements, the research on the treatment of wastewater with the technology of "initial oxidation+pretreatment+biochemical treatment" was carried out to explore the wastewater with different ozone, catalytic oxidation time and different hydraulic retention time. Moreover, the influence of wastewater reuse after treatment on mineral processing index was investigated, and the feasibility of the process was evaluated. The results show that O3 was used to directly or indirectly oxidize the residual organic chemicals in the wastewater in the initial oxidation, ; the co-pretreatment removes Ca2+ and heavy metals in the wastewater; the subsequent biochemical treatment further improves the quality of the water. In addition, the ozone concentration is 60 mg/L, the catalytic oxidation time is 20 min, and the hydraulic retention time is 16.71 h, which can reduce the wastewater COD concentration to 34.32 mg/L, and the removal rate is 91.9%. Further research shows that the increase in hydraulic retention time and ozone concentration significantly improves the wastewater treatment effect. Reusing the treated wastewater for ore beneficiation can effectively eliminate the influence of reused water on the instability factors of ore beneficiation, and it is close to the beneficiation index of clean water. Under stable operation, this process can not only realize the efficient treatment and reuse of mineral processing wastewater, but also has a lower processing cost of 2.65 ¥/m3, which can provide usable technical experience for the reuse of wastewater from domestic lead-zinc processing plants.
-
1. 引言
氟作为自然界中分布最广泛的元素之一,主要以阴离子(F-)存在于萤石(CaF2)、冰晶石(Na(AlF6))、以及氟磷灰石[Ca10(PO4)6F6]等矿物中。氟元素是电负性最大的元素,化学性质活泼,极易与金属元素或无机元素发生反应[1, 2]。氟是生物生命体活动所必需的微量元素之一。人体摄入氟主要来源于饮水,氟在人体中主要分布于牙齿和骨骼中,适量的摄入氟元素,有利于维持正常的新陈代谢,对人体生长发育具有一定促进作用,但是人体若长期饮用高氟水,会造成各种疾病,比如氟斑牙、氟骨病,甚至导致氟中毒[3, 4]。世界卫生组织(WHO)的规定,饮用水中氟化物的最大允许浓度为1.5 mg/L。
针对含氟废水,国内外研究者已经研究出多种治理技术,目前主要包括沉淀法、吸附法、离子交换法、膜分离法和电化学法等。各种除氟工艺技术拥有各自的优势和局限性[5-7]。比如,膜分离或电化学等方法能够实现深度脱氟,但工艺复杂,成本偏高,大规模应用有困难。沉淀法操作简单,成本低,能够大规模应用,但受限于沉淀物氟化钙的溶解度,出水浓度一般在8~9 mg/L,不能达到饮用水的标准。混合药剂沉淀是一种近些年来提出的沉淀方法。将钙盐和其它可以沉淀氟离子的盐类,例如镁盐、铝盐和磷酸盐等混合使用作为沉淀剂。混合药剂会产生溶解度不同的沉淀,促进了整体沉淀反应的进行,同时可能产生的沉淀对氟化物沉淀有吸附作用,相比单一使用某种盐除氟的效果更好。通过使用氯化钙和磷酸盐联合药剂法处理含氟废水,钙离子、氟离子和磷酸根离子反应生成了氟磷酸钙沉淀,反应后的氟离子浓度可以降到5 mg/L[8, 9]。
机械力活化的手段越来越受到各方面的关注,利用机械能来诱发化学反应,或者诱导材料组织、结构和性能的变化,以此来制备材料或对材料进行改性处理,在非金属矿的加工利用方面有不少报道[10-12]。通过机械力化学法,将Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3在介质的作用下发生摩擦、碰撞等一系列物理化学反应、活化,促使材料晶格结构破坏致使其发生化学反应形成Ca-Al复合材料,并对低浓度的含氟废水进行高效率的除氟。这种工艺的开发,为材料的利用提供新的途径,为研究深度脱氟脱氟材料提供了一种新的思路,并对改善饮用水条件具有重要意义。
2. 试验材料和方法
球磨Ca-Al复合材料所用试剂: 氢氧化钙[Ca(OH)2]、氢氧化铝[Al(OH)3],均为分析纯,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。高岭土原料来自于湖南某高岭土矿,经XRD物相分析,样品中无杂质相,化学组成成分见表 1,其中Al2O3、SiO2和含水量非常接近高岭石的理论组成。
表 1 高岭土样品的主要化学成分Table 1. Main chemical compositions of kaolin sampleComposition Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 SO3 Mass/% 0.14 0.19 36.91 45.50 0.16 0.86 Composition K2O CaO TiO2 Fe2O3 LOI Mass/% 0.24 0.44 1.15 0.59 13.82 球磨活化Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3的试验是在行星式球磨机(飞驰P-7,德国产)中进行,具体试验操作如下: 总质量为4 g的Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3按照一定比例添加于球磨罐中,球磨转速为600 r/min,Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3的比例按照Ca : Al摩尔比为3 : 1、3 : 2、3 : 3;球磨时间分别为10 min、1 h、2 h,及研钵研磨10 min。球磨活化Ca(OH)2和高岭土制备Ca-Al复合材料的试验在类似的试验条件下进行,其中高岭石中间的Al和Ca的摩尔比和双氢氧化物的Ca-Al摩尔比一致。
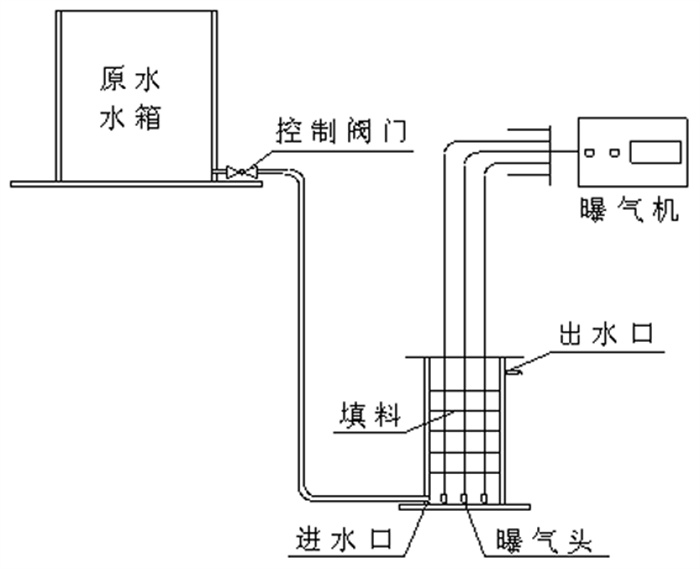
脱氟试验在常温下进行,在浓度为10 mg/L、体积100 mL的氟离子溶液中添加0.5 g的制备样品,于磁力搅拌器上500 r/min进行搅拌到所定时间。然后,取适量溶液进行离心,将离心后的上层清液进行氟离子浓度测试,使用氟离子选择性电极(PXSJ-216F, 上海雷磁),参照《水质氟化物的测定离子选择电极法》(GB7484—1987)。搅拌后的沉渣过滤于烘箱中烘干,和球磨样品同样进行XRD、TG等测试分析。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 氢氧化铝为铝原料
3.1.1 Ca : Al摩尔比对材料脱氟性能的影响
首先探索了Ca : Al摩尔比对材料脱氟性能的影响,从图 1中可以看出,单一的Ca(OH)2在搅拌反应2 h后只能将氟离子的浓度降到8.7 mg/L,在Ca(OH)2里添加Al(OH)3,明显提高了氟离子的去除效果,随着Ca : Al摩尔比的增加氟离子的残留浓度降低。在Ca : Al摩尔比为3 : 2时,氟离子的残留浓度降低到0.62 mg/L。Ca : Al摩尔比增加到3 : 3时与3 : 2时相比,效果不再明显变化。这表明,球磨后的Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3所制备的Ca-Al复合材料参与了深度脱氟的反应,相比Ca(OH)2的以氟化钙为沉淀产物的脱氟反应会受限于氟化钙溶度积的影响,平衡浓度居高不下,不能达到标准,而合成的材料能将氟离子浓度降到1 mg/L以下,在Ca : Al摩尔比为3 : 2时,脱氟可以达到饮用水的氟含量标准,考虑到氢氧化铝的成本因素,确定Ca : Al摩尔比3 : 2为后续试验所用比例制备材料。
3.1.2 球磨时间对材料脱氟性能的影响
材料制备的球磨时间也是影响去除氟效果的关键因素。球磨时间作为变量,将球磨时间设置为10 min、1 h、2 h来制备材料,并和原料的手混样品进行对比。随着球磨时间的加长,材料中颗粒的粒径逐渐减小、比表面积变大,当球磨时间超过一定值时,比表面积增大不再是主要现象,高能球磨下可能诱导固相化学反应,因此需要确定最佳的球磨时间,获得对脱氟有效的物质组成。
试验结果如图 2所示。当Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3充分混合10 min,残余的氟离子浓度约为5.8 mg/L,是Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3在氟离子溶液中协同作用达到的除氟效果。将Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3进行球磨,随着球磨时间的增加,氟离子的剩余浓度降低,明显提高了去除氟离子的能力。样品球磨1 h,搅拌反应2 h,就可以降到0.72 mg/L,样品的去除效果最好,达到饮用水的氟含量标准。球磨2 h的材料去除氟离子的剩余浓度不再明显降低。随着搅拌反应时间的增加,氟离子浓度逐渐降低,在搅拌2 h时后氟离子浓度趋于平稳,达到稳定状态。因此,基于能耗考虑,确定球磨时间1 h为最佳条件。
3.1.3 机理分析
通过以上试验确定了制备的材料具有深度脱氟的能力,为了解所制备材料的组成物相,对Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3的摩尔比为3 : 2,球磨时间为1 h条件下所制备的材料进行XRD测试分析。材料的XRD图谱如图 3所示。从图中可以看出材料的中能确认的特征峰除了一部分原料Ca(OH)2之外,生成物为钙铝复合氢氧化物Ca3Al2(OH)12新物质(矿物名称加藤石: katoite),而原料中的Al(OH)3经过球磨之后不能在图谱中观察到。从原材来看,Ca3Al2(OH)12是Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3经过球磨所产生的物质,并且是所用原料中元素的比例,而这种新生成的物质应该是将氟离子在低浓度的情况下进行高效去除的主要原因。
为了对比合成得到的加藤石物相和一般氢氧化钙去除氟离子能力的差异,并考虑到氟离子溶液的初始浓度对材料脱氟效果有重要的影响,将材料在含有100 mg/L、1 000 mg/L的含氟溶液及超纯水中进行搅拌反应2 h后所得的沉淀物进行分析,图 4显示了材料处理不同浓度氟离子溶液后的沉积物的XRD图谱。
由图 4可知,沉淀物中的物相有katoite(Ca3Al2(OH)12)、CaF2和Ca-Al双氢氧化物/或水滑石(Ca/Al LDH)。材料在超纯水中搅拌以后,主要产生了Ca/Al LDH的峰和Ca3Al2(OH)12的峰;处理100×10-6 g/L的氟离子溶液以后的沉积物,产生了Ca/Al LDH的峰和Ca3Al2(OH)12的峰,其XRD图谱出现的峰形基本上与前者一致,但峰强明显变弱;对于处理1 000×10-6 g/L的氟离子溶液以后的沉积物,XRD图谱中有明显增加的CaF2的峰,CaF2峰的峰强很强,相比之下其它相的峰的峰强很微弱。通过对比3种沉淀物加藤石相的峰,选择了加藤石的521结晶面放大绘制了清晰图,可以明显看到峰向高角度偏移,说明加藤石的晶相形态发生了改变,参与了化学反应。可以推断出,F-进入Ca3Al2(OH)12替换了OH-,F-和OH-的半径不同,使其结晶面间距发生了变化,XRD的峰形产生了明显的偏移。相比3种沉淀物的Ca/Al LDH的峰相,也选择了图谱中属于LDH的最强峰另外绘制了清晰可确认的图,没有发现到峰的偏移,并且峰强逐渐变弱,直至消失。这可以理解为,随着氟离子的浓度升高,会消耗更多Ca(OH)2,从而抑制Ca/Al LDH的生成至消失,并且Ca/Al LDH没有参与去除氟离子的反应中。材料中只有Ca(OH)2和Ca3Al2(OH)12参与了脱氟的反应。
根据所得到的推测,可以列出以下反应式:
$$ \mathrm{Ca}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{~F}^{-}=\mathrm{CaF}_{2} $$ (1) $$ \mathrm{Ca}_{3} \mathrm{Al}_{2}(\mathrm{OH})_{12}+x \mathrm{~F}^{-}=\mathrm{Ca}_{3} \mathrm{Al}_{2} \mathrm{~F}_{x}(\mathrm{OH})_{12-{x}}+x \mathrm{OH}^{-} $$ (2) 当氟离子浓度高的时候,反应式(1)为主要反应,消耗大量Ca(OH)2生成CaF2;当氟离子浓度低时,反应式(2)为主要反应,生成Ca3Al2 Fx(OH)12-x降低氟离子浓度。由此看出,样品中的加藤石在对低浓度氟离子溶液去除氟离子中起关键作用,发生的离子交换作用不同于高浓度时氟化钙沉淀的机理,才能实现残留氟离子浓度低于1 mg/L的水准。
3.1.4 共存阴离子对材料除氟性能的影响
氟污染水体中成分复杂,通常含有硫酸根、磷酸根或氯离子等多种共存离子。氟化钙沉淀的除氟工艺,阴离子会与氟离子产生竞争关系,影响材料除氟的性能。研究了这些共存离子对新合成材料脱氟的影响,结果如图 5所示。材料的脱氟结果是0.32 mg/L,当溶液中含有共存离子时,对其产生轻微影响。在PO43-存在时,氟离子浓度降到0.35 mg/L,几乎没有影响。在Cl-、SO42-、CO32-存在时,剩余的氟离子大于不存在共存离子的的浓度,共存离子的存在对材料除氟效果只有轻微抑制作用。这可以理解为,PO43-、CO32-、SO42-尽管和F-竞争Ca2+,对合成的加藤石产品并没有表现出来竞争力,残余的氟离子的浓度均在1 mg/L以下,符合饮用水中氟含量的标准。这也间接证实了氟化钙沉淀机理不再是主要因素,共存的阴离子即便和钙离子有较强的吸附沉淀作用,减少了水相中的钙离子浓度,对合成的样品脱氟效果的影响极小,加藤石中的羟基和氟离子的交换作用成为主要机理,原则上不再受钙离子浓度的影响,进而也就不受和钙离子有亲和作用的阴离子的影响。显示材料对氟离子的选择性很好。
3.2 高岭石为铝原料
三水铝石作为氢氧化铝的原料可以用来制备上述深度脱氟材料,我国铝土矿资源虽然丰富,但三水铝石的储量较低,需要考虑来源更为丰富的原料。黏土矿物高岭石中间含有氢氧化铝成分,以前的机械力活化高岭石等层状含水硅酸盐矿物的研究中,已经确认这一类矿物比较容易非晶化以及和氢氧化钙之间的化学反应。这里用高岭石替代氢氧化铝,探讨了合成深度脱氟材料的可能性。
3.2.1 Ca(OH)2和高岭土的比例对材料脱氟性能的影响
首先考察了Ca(OH)2和高岭土的比例对材料脱氟性能的影响,为了探究材料中钙铝的最佳比例,以达到脱氟最佳效果,将Ca与高岭土中Al含量的摩尔比作为变量条件,按照Ca : Al摩尔比为3 : 1、3 : 2、3 : 3的比例进行添加,制备材料,搅拌反应时间为12 h。试验结果如图 6所示。从图中可以看出,单一的Ca(OH)2在搅拌反应12 h后,氟离子的浓度降到5.5 mg/L,高岭土和Ca(OH)2混合球磨的样品明显将氟离子的浓度降了下来,提高了氟离子的去除效果。在Ca : Al摩尔比为3 : 2时,氟离子的残留浓度达到1.6 mg/L,降到了最低,达到了最佳效果,而Ca : Al摩尔比为3 : 1、3 : 3时的脱氟效果没有Ca : Al摩尔比为3 : 2时的脱氟效果好。这可以确定球磨后的Ca(OH)2和高岭土可以对低浓度的氟离子进行去除,提高了原料的去除效率。通过本次试验确定Ca(OH)2和高岭土的最佳摩尔比例为Ca : Al摩尔比3 : 2,后续试验探究中按此比例制备材料。
3.2.2 机理分析
将球磨材料进行XRD测试分析,所得到的XRD图谱如图 7所示。从图中可以看出,原料高岭石的特征峰全部消失,意味着高岭石和Ca(OH)2之间发生了反应。图谱中特征峰为残存没有反应的Ca(OH)2和新物质加藤石相,可以理解为球磨中Ca(OH)2和高岭土反应生成了新的物质,即成分为Ca3Al2(OH)12的加藤石。和3.1节使用化学试剂氢氧化铝相比,使用高岭石的结果虽然很相近,但也有所不同,一个是氟离子残存浓度略高,超过了1×10-6 g/L;另外,经过同卡片上加藤石相的峰进行对比,可以确认到峰向高角度偏移。高岭石和氢氧化钙的球磨反应产物加藤石相主要涉及到高岭石中的铝的参与,但和纯氢氧化铝的结果上的不同,让我们有理由推测高岭石的硅酸根也可能参与了反应,生成相同结构但成分更为复杂的石榴子石相。新生成的加藤石中间的羟基同样能同溶液中的F-进行离子交换,提高了在低浓度氟离子溶液除氟的效率。这就是材料能够深度除氟的主要原因。只是硅酸根参与后的石榴子石相中间的羟基含量会低于纯加藤石相,在深度脱氟效率上略有下降,但是仍远高于氟化钙沉淀的脱氟效果。
为了进一步确定材料中的物质组分,将球磨Ca(OH)2和高岭土所制备的材料和只进行简单混合的Ca(OH)2和高岭土所制备的材料进行TG-DSC热重分析,测试结果如图 8所示。
由图 8(a)可知,原料的TG曲线出现了2个阶段的质量损失,350~450 ℃之间的质量损失与Ca(OH)2脱水有关,损失7.47%的质量,450~650 ℃之间的质量损失与高岭土内羟基的脱出有关,损失12.08%的质量。相比之下,球磨后的材料从80 ℃开始呈现出连续平缓的质量损失,到680 ℃损失了21.09%的质量,这与原样的TG曲线相差颇大,这样的连续质量损失揭示了作为原料的Ca(OH)2和高岭土在样品里已经消失,球磨作用诱导了它们之间的结合,生成了新的物质。图(b)DSC的结果也有很大的变化,不仅峰值个数增加,且温度位置也有所变化,因此可以确定,通过球磨Ca(OH)2和高岭土所制备的样品中有新物质的存在,进一步佐证了材料能够深度脱氟的推测。
4. 结论
机械力球磨Ca(OH)2和Al(OH)3,在Ca : Al摩尔比为3 : 2、转速500 r/min的条件下球磨1 h可获得高效脱氟材料,加入到氟离子起始浓度为10 mg/L的溶液经搅拌2 h后能降到0.32 mg/L,实现高效率的脱氟,满足饮用水中氟含量限值要求。通过测试分析,球磨生成的加藤石相Ca3Al2(OH)12经过F-与Ca3Al2(OH)12中的羟基的离子交换,理解为脱氟的主要途径,不同于传统含钙物质的氟化钙沉淀的脱氟机理,这一新的脱氟机理是实现深度脱氟满足饮用水的含氟要求的原因所在。
-
表 1 水力停留时间方案
Table 1 Hydraulic retention time scheme
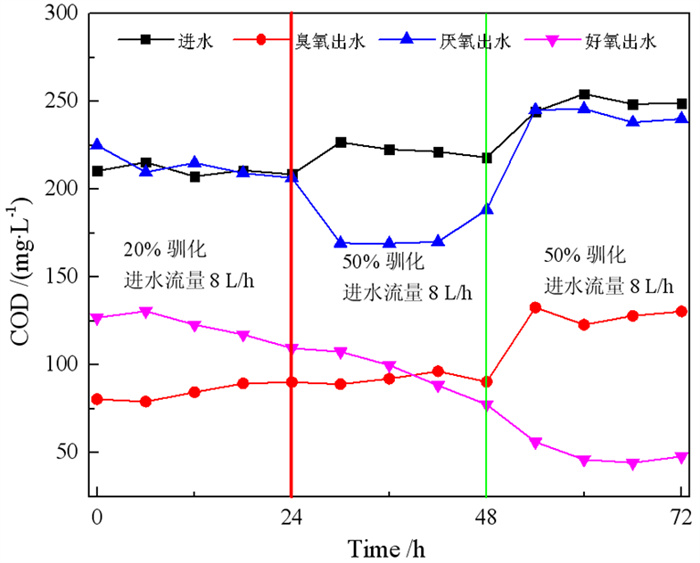
工艺阶段 HRT /h 方案1 方案2 方案3 进水 2.25 1.7 0.85 臭氧出水 1.13 0.8 0.42 厌氧出水 10 8 4 好氧出水 3.33 2.5 1.25 注:进水,指选矿废水进入臭氧催化反应器的阶段;臭氧出水,指水臭氧催化反应器阶段;厌氧出水,预处理阶段和厌氧反应阶段;好氧出水,水好氧反应阶段;HRT,水力停留时间。 表 2 废水水质分析
Table 2 water quality analysis
/(mg·L-1) 成分 固含率/% pH COD TOC Fe2+ Pb Zn Cu Cr 硫尾水 0 6.85 642.24 15.63 0.353 4.45 7.27 nd nd 2#池水 0.006 7 12.19 367.24 19.65 0.197 1.44 nd nd nd 硫精水 0.011 6 8.04 314.65 35.98 0.119 0.86 nd nd nd 试验用水 0.006 2 10.07 397.45 21.29 0.211 1.872 1.073 nd nd 成分 Cd Mn K+ Na+ Ca2+ F- Cl- SO42- NO3- 硫尾水 nd 2.17 122.98 32.17 809.4 0.46 13.23 84.70 30.80 2#池水 nd nd 43.96 13.39 578.3 0.66 3.95 65.19 17.50 硫精水 nd 0.26 51.91 15.32 664.8 nd 2.51 54.56 13.75 试验用水 nd 0.352 57.19 16.83 628.46 0.52 5.19 65.39 19.107 表 3 不同水力停留时间对COD去除的影响
Table 3 Effect of different hydraulic retention time on COD removal
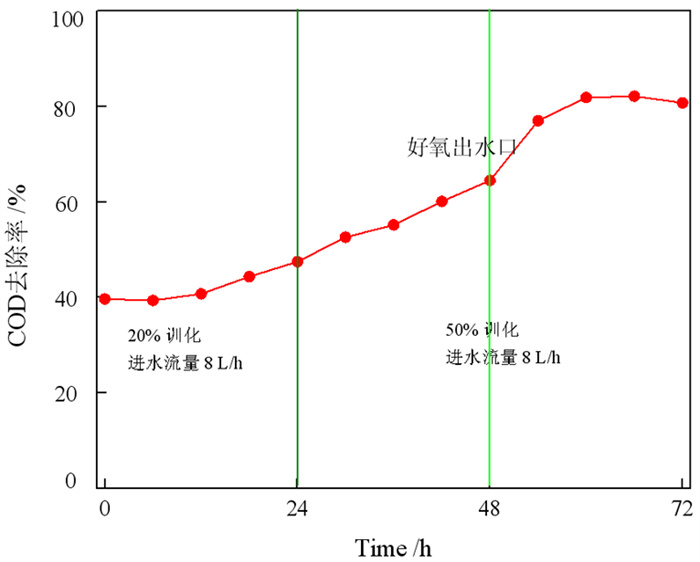
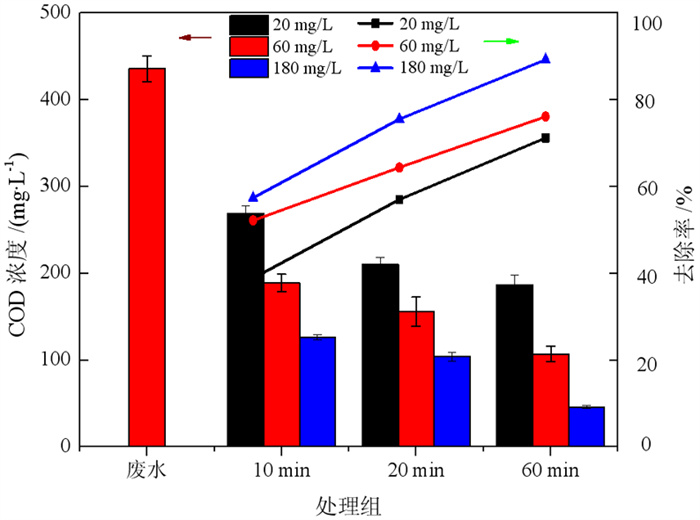
方案 名称 COD/(mg·L-1) 去除率/% HRT/h 进水 424.44 - 2.25 臭氧出水 151.96 64.2 1.13 方案1 厌氧出水 141.48 66.7 10 好氧出水 34.32 91.9 3.33 进水 445.4 1.7 臭氧出水 145.9 67.2 0.8 方案2 厌氧出水 138.2 68.9 8 好氧出水 62.16 86.1 2.5 进水 460.8 0.85 臭氧出水 253.44 45.0 0.42 方案3 厌氧出水 207.2 55.0 4 好氧出水 51.26 88.9 1.25 表 4 出水水质分析
Table 4 Analysis of effluent quality
/(mg·L-1, 除pH外) 出水 pH Ca Fe Cu Zn Pb CODcr NH3-N TP SS 本工艺 7.10 655 2.14 1.52 0.71 1.44 35.4 10.3 0.48 15.5 对比1 6.52 712 3.05 1.43 0.88 1.26 52.1 15.2 0.55 37.8 对比2 4.55 805 3.67 1.99 0.52 1.70 80.5 12.6 1.41 55.1 表 5 废水处理回用选矿试验结果
Table 5 test results of wastewater treatment and reuse beneficiation
产品 Q/g γ/% 品位/% 金属量 回收率/% Pb Zn Pb Zn Pb Zn K铅精矿 95.50 6.03 61.95 2.45 373.5 14.8 84.4 1.7 清水 K锌精矿 226.00 14.27 1.01 58.47 14.4 834.3 3.3 95.3 尾矿 1 262.40 79.70 0.68 0.33 54.5 26.0 12.3 3.0 原矿 1 583.9 442.4 875.1 100.0 100.0 K铅精矿 98.50 6.20 60.94 2.31 378.0 14.3 83.8 1.6 本工艺 K锌精矿 227.00 14.30 1.21 58.16 17.4 831.4 3.8 95.5 尾矿 1 262.40 79.50 0.70 0.32 55.6 25.2 12.3 2.9 原矿 1 587.9 450.9 870.9 100.0 100.0 K铅精矿 115.00 7.34 54.31 3.58 398.8 26.3 87.7 3.0 对比1 K锌精矿 240.00 15.33 0.56 51.75 8.6 793.1 1.9 91.8 尾矿 1 211.00 77.33 0.61 0.58 47.2 44.9 10.4 5.2 原矿 1 566 454.6 864.2 100.0 100.0 K铅精矿 132.00 8.46 49.19 3.52 416.0 29.8 91.3 3.4 对比2 K锌精矿 269.00 17.23 0.37 47.02 6.4 810.3 1.4 93.8 尾矿 1 160.00 74.31 0.45 0.32 33.4 23.6 7.3 2.7 原矿 1 561 455.8 863.6 100.0 100.0 表 6 小试试验经济成本核算
Table 6 economic cost accounting of pilot test
项目 臭氧成本 生化成本 活性炭成本 砂滤成本 药剂成本 总计 参考文献 费用/ (元·m3) 1.0 0.6 0.5 0.3 0.25 2.65 本研究 统计结果 2.20 [20] 调查结果 2~3 [21] 注:臭氧成本是基于经验成本。 -
[1] 史宇驰, 邹勤, 陶镇, 等. 湖南某多金属矿选矿废水处理回用试验研究[J]. 中国钨业, 2015, 30(5): 34-38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0622.2015.05.006 [2] 顾泽平. 含苯胺黑药废水的物化净化特性研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2006: 41-42. [3] 张辉, 周晓彤, 邱显扬. 多金属硫化矿选矿废水处理的研究现状[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2015, 9(4): 226-230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2015.04.004 [4] 张东方, 陈涛. 接触氧化法处理铅锌矿选矿废水试验研究[J]. 广东化工, 2012, 39(6): 285-287. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2012.06.154 [5] 敖顺福. 典型铅锌选矿厂废水零排放工艺对比分析[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(1): 38-45. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=260f7f81-fd8f-4e18-8b3b-f12425818d7b [6] 陈伟, 彭新平, 陈代雄. 某铅锌矿选矿废水处理复用与零排放试验研究[J]. 环境工程, 2011, 29(3): 37-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201103013.htm [7] 杨建文. 盘龙铅锌矿铅锌选矿废水处理及循环回用研究[J]. 有色金属工程, 2018(2): 133-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YOUS201802027.htm [8] 华金铭, 魏可镁, 郑起, 等. 物化-生化组合工艺处理提铜选矿药剂生产废水中试验研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(1): 207-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201301039.htm [9] 张辉, 周晓彤, 邱显扬. 多金属硫化矿选矿废水处理的研究现状[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2015, 9(4): 226-230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2015.04.004 [10] 严群, 桂勇刚, 周娜娜, 等. 混凝沉淀法处理含砷选矿废水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(9): 3683-3688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201409026.htm [11] 张艳, 戴晶平, 张康生. 凡口矿选矿废水处理与利用试验研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2008, 28(3): 45-48. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2008.03.012 [12] 黄红军. 广东某铅锌矿选矿废水资源化处理[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2012(2): 37-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL201202012.htm [13] 冯秀娟, 刘祖文, 朱易春. 混凝剂处理选矿废水的研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2005, 25(4): 27-29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2005.04.008 [14] 王自超, 刘兴宇, 宋永胜. 臭氧生物活性炭工艺处理某多金属硫化矿浮选废水的小试研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(5): 1723-1728. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201305025.htm [15] 阳承胜, 蓝崇钰. 宽叶香蒲人工湿地对铅/锌矿废水净化效能的研究[J]. 深圳大学学报: 理工版, 2000(Z1): 51-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZDL2000Z1009.htm [16] 林伟雄, 许娉婷, 武纯. 采用浸没式膜生物反应器处理苯胺黑药浮选废水[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016(11): 2461-2468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201611024.htm [17] Gunten, U. V. (2003). Ozonation of drinking water: part I. Oxidation kinetics and product formation[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(7): 1443-1467. DOI: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00457-8
[18] 王亮华, 许伟航, 傅平丰, 等. 浮选废水中共存离子对臭氧氧化苯胺黑药的影响研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(1): 1-8. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=a912f08e-6ddb-4710-8752-3323066a31fd [19] 姜智超, 余侃萍, 张玉凤. 臭氧氧化-循环喷淋法处理钨钼选矿废水[J]. 矿冶工程, 2020, 40(3): 75-78. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2020.03.020 [20] 雷金勇, 王利国, 黄伟, 等. 铅锌矿选矿废水的节水工艺与重金属的低成本处理技术[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2016(6): 64-65. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2016.06.046 [21] 潘菊芬. 铅锌矿选矿废水的节水工艺与重金属的低成本处理技术分析[J]. 世界有色金属, 2018(5): 24-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201805014.htm




 下载:
下载: